The Opportunity for Intelligent Aviation Hubs
Modern airports operate as complex logistical hubs. They synchronize thousands of moving parts daily, including passengers, aircraft, baggage, and staff. Traditional management methods struggle to keep pace with this complexity. They often rely on reactive, manual processes that cannot handle rising passenger volumes and dynamic security threats. This creates operational bottlenecks and diminishes the passenger experience.
The strategic implementation of AI for airports offers a transformative solution. It moves operations from a state of reactive problem-solving to proactive, data-driven optimization. This is not just an incremental upgrade. Instead, it represents a fundamental shift toward creating truly intelligent aviation environments. An integrated approach to AI for airports is becoming a competitive necessity. It unlocks new levels of efficiency, security, and passenger satisfaction that legacy systems cannot achieve.
1. The Challenge: Navigating Complexity in Modern Airport Operations
Understanding the need for advanced technology begins with recognizing the immense pressures on today’s airports. The successful application of AI for airports directly addresses the core challenges inherent in this high-stakes environment.
Context: The High-Stakes Airport Environment
Airports are critical national and international infrastructure. They process millions of people and vast quantities of cargo, making them complex logistical puzzles and high-value targets for security threats. Airport managers must constantly adapt to evolving regulations, environmental standards, and technological shifts. This dynamic nature demands solutions that offer both flexibility and robust performance. The sheer scale of operations means that even small inefficiencies can trigger cascading delays, costing airlines and the airport millions.
Key Pain Points Faced by Airports :-
- Persistent Security Vulnerabilities. Airports face a constant barrage of threats. These range from physical perimeter breaches and unattended luggage to sophisticated cybersecurity attacks.
- Passenger Flow Bottlenecks. Large crowds create long queues at check-in counters, security checkpoints, and boarding gates. These bottlenecks frustrate passengers and negatively impact their overall travel experience.
- Critical Airside Safety Risks. The airside environment presents unique dangers. These include Foreign Object Debris (FOD) on runways, wildlife strikes, and unauthorized intrusions into restricted areas, all of which pose a direct threat to aircraft safety.
- Pervasive Logistical Inefficiencies. Coordinating disparate operations like baggage handling, air traffic control, and gate allocation is a monumental task. Minor delays in one area can cause significant, system-wide disruptions.
- Costly Resource Misallocation. Airports often struggle to schedule staff, gates, and other key resources to match fluctuating, real-time demand. This leads to unnecessary operational costs and gaps in service quality.
Limitations of Traditional Approaches
Legacy systems fail because they are fundamentally disconnected from the airport’s dynamic reality. Traditional methods rely on manual monitoring by human operators, which is susceptible to fatigue and error. Furthermore, they use static planning models based on historical averages. These models cannot adapt to unpredictable, real-time events like sudden flight delays or passenger surges. For instance, scheduled runway inspections for FOD are inherently flawed. A dangerous object can appear at any moment between checks, creating a significant safety gap. Traditional systems are effectively “data blind.” They lack the senses to perceive and the brain to process the massive streams of real-time data that define a modern airport’s operational landscape. This is the core limitation that AI for airports overcomes.
2. Our AI Solution Concept: The Unified Airport Intelligence Platform
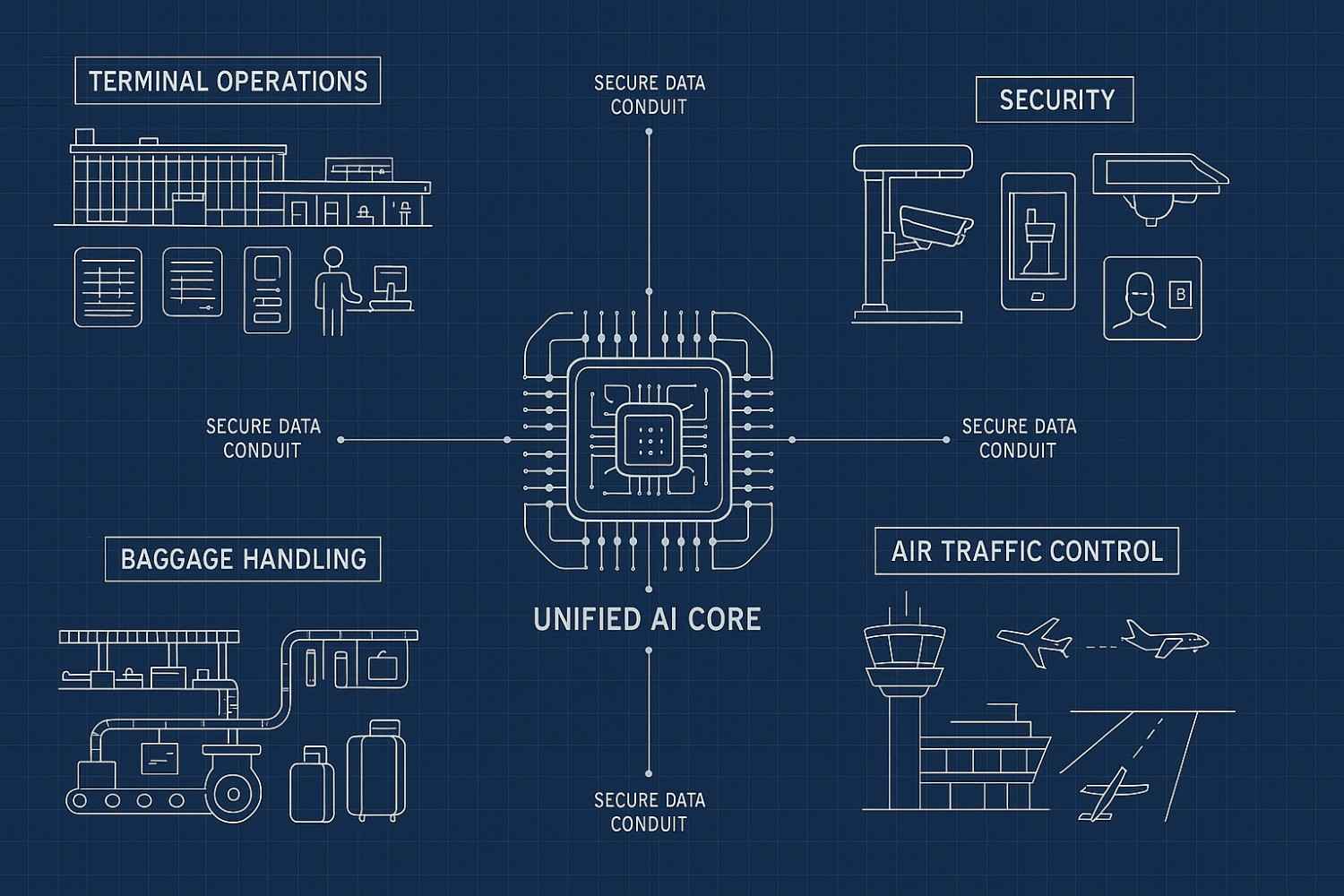
Instead of deploying disconnected tools, the most effective approach involves an integrated system. This platform acts as a central nervous system for the entire airport. It provides a holistic, real-time view of all key operations. This vision for AI for airports moves beyond single-point solutions.
Vision & Objectives for an AI-Powered System
The ultimate vision is to create a unified platform that integrates data from security, passenger flow, airside safety, and general operations. This system empowers airport staff with the tools to make proactive, data-driven decisions that enhance every facet of the airport experience.
Key objectives of such a platform include:
- Unify Disparate Data Streams. The system must break down information silos. It achieves this by integrating feeds from CCTV cameras, IoT sensors, flight schedules, and other legacy airport systems.
- Enable Proactive Threat Mitigation. It aims to shift the airport’s security posture from reactive to proactive. The system automatically detects and flags potential threats in real time before they can escalate.
- Optimize the Entire Passenger Journey. The platform seamlessly manages passenger movement from the moment they arrive at the curb to the time they board their flight, minimizing wait times and reducing travel stress.
- Maximize Overall Operational Efficiency. It automates and optimizes the allocation of critical resources. This includes smart baggage handling, dynamic gate assignments, and intelligent energy consumption to reduce costs and delays.
- Empower Human Decision-Makers. The platform provides staff with clear, actionable insights and powerful decision support tools. This allows them to focus on strategic management and complex exception handling rather than tedious manual monitoring.
The following table provides a high-level overview of how a unified platform addresses key airport challenges.
| Solution Area | Problem Solved | Core Technologies | Primary Benefit |
| Advanced Security | Unattended threats, suspicious behavior | Computer Vision, Anomaly Detection, Machine Learning | Proactive Threat Mitigation |
| Crowd Management | Congestion, long queues, poor passenger flow | Vision AI, Density Monitoring, Predictive Analytics | Enhanced Passenger Experience |
| Runway & Perimeter Safety | FOD, intrusions, wildlife strikes | AI-FOD Systems, PIDS, Thermal/Optical Sensors | Increased Airside Safety |
| Operational Optimization | Baggage mishandling, gate delays, energy waste | AI Image Recognition, RFID, Optimization Algorithms, IoT | Drastic Efficiency Gains |
3. How It Works: A Closer Look at all AI Solutions for Airports
An integrated AI for airports platform is composed of several specialized modules. Each module targets a specific set of challenges using tailored technologies and processes. Here is a detailed look at how these key solutions function.
3.1 Solution 1: AI for Airport Security and Threat Detection
This solution transforms standard surveillance systems from passive recorders into active, intelligent sentinels. The use of AI for airport security provides a powerful layer of automated oversight.
Data Acquisition: Existing Surveillance Infrastructure
First, the system intelligently leverages an airport’s existing CCTV systems. This approach minimizes the need for costly new hardware installations, making it a highly practical upgrade.
How does the AI work:-
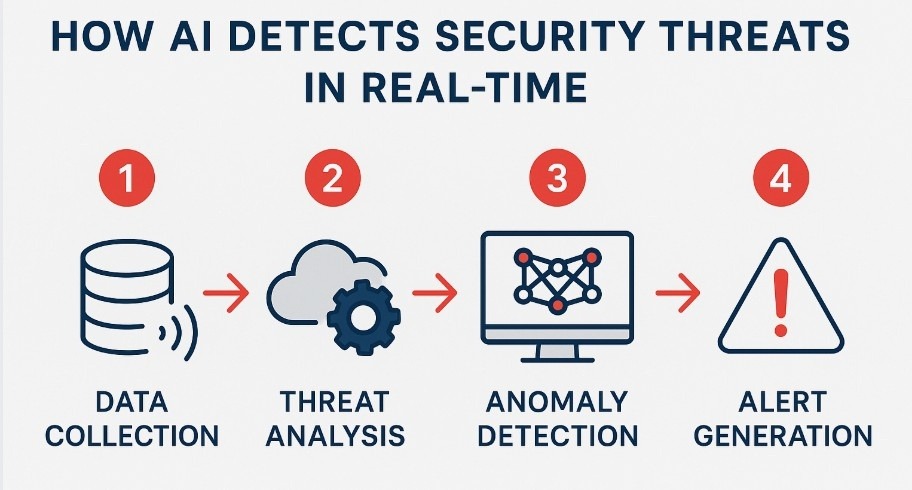
The system processes video data through a multi-stage pipeline to identify threats.
- The AI ingests and analyzes real-time video streams from dozens or hundreds of cameras simultaneously.
- Next, it uses a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) (A type of deep learning model highly effective at processing and analyzing visual imagery) to perform object detection. The CNN identifies and classifies objects within each frame, such as people, backpacks, and suitcases. Advanced models like YOLO (You Only Look Once) provide the speed needed for real-time analysis.
- The system then employs a tracking algorithm. This algorithm associates objects across multiple frames, for example, by linking a specific bag to the person who set it down.
- Finally, the system applies anomaly detection algorithms. An “unattended luggage” alert triggers if a bag remains stationary for a preset duration (e.g., 30 seconds) after its owner moves a significant distance away. To detect “suspicious activities,” the AI uses behavioral recognition to flag actions that deviate from normal patterns. This includes individuals loitering in restricted zones, moving against the flow of a crowd, or exhibiting sudden, erratic movements.
Output & Interaction: Actionable Intelligence
When the AI confirms an anomaly, it generates an immediate, automated alert. This alert is sent to a central security command center. It includes the specific camera feed, a precise timestamp, the location, and a clear description of the threat.
3.2 Solution 2: AI for Airport Crowd Management
This module uses AI for airports to turn chaotic passenger flow into a predictable and manageable system, directly improving the passenger experience.
Data Acquisition: The Eyes of the Terminal
The system pulls continuous video feeds from cameras strategically placed at known chokepoints. These include check-in halls, security screening queues, customs and immigration lines, and busy departure gate areas.
How does the AI work:-
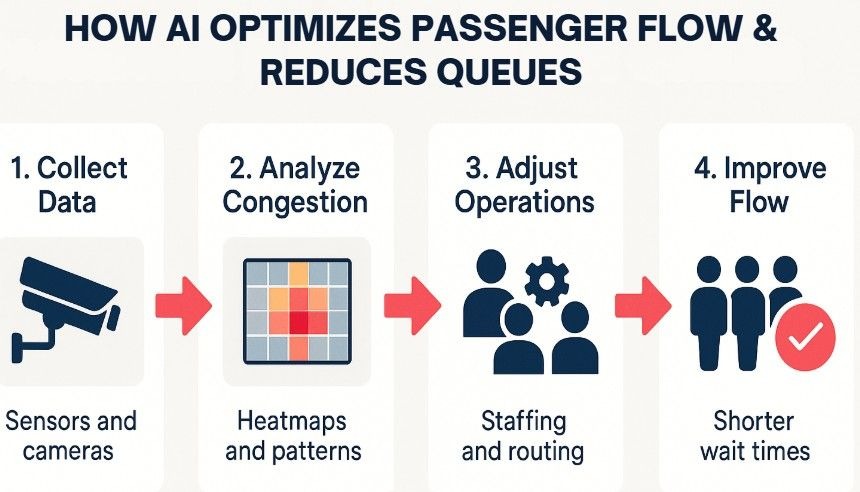
- First, the AI applies computer vision models to the video streams to perform real-time people counting and density estimation. It accurately calculates the number of individuals in defined zones and measures throughput rates.
- For queues, the AI specifically analyzes key metrics. It measures the number of people waiting, the physical length of the line, and the average wait time for each passenger.
- Next, the system uses machine learning models to create predictive forecasts. It combines this real-time data with historical trends and flight schedule information to anticipate future congestion points, effectively predicting passenger surges before they happen.
- The system then visualizes all this data as a simple, intuitive heatmap of the terminal. This map uses colors to show areas of high passenger concentration (red) versus areas with smooth, free-flowing traffic (green).
Output & Interaction: Dynamic Resource Allocation
Operations managers view these predictive insights and live heatmaps on a central dashboard. This allows them to take proactive measures. For example, they can open additional security lanes to handle an anticipated rush or use digital signage to guide passengers toward less crowded pathways, ensuring a smoother journey.
3.3 Solution 3: AI for Airport Runway & Perimeter Safety
This solution provides a persistent, all-weather watch over the airport’s most critical and vulnerable areas. This application of AI for airports is essential for preventing catastrophic accidents.
Data Acquisition: A Multi-Sensor Approach
This system integrates data from a variety of specialized sensors installed along runways and perimeter fences. It uses high-definition electro-optical (EO) cameras for clear daylight conditions and advanced thermal cameras for operation at night or in low-visibility situations.
How does the AI work: –
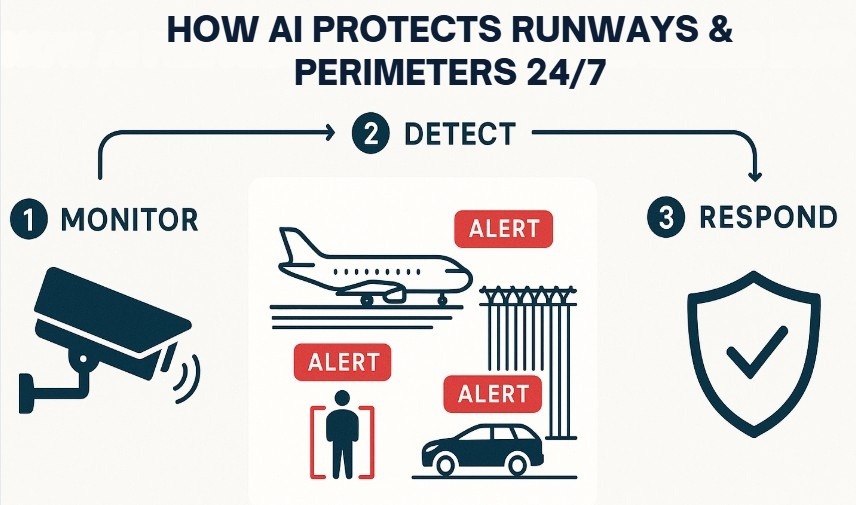
- The AI-powered system tirelessly scans the runway and perimeter surfaces 24/7, analyzing a constant stream of image and sensor data.
- For FOD detection, the AI is trained to recognize the unique visual and thermal signatures of small, anomalous objects. It can spot items like metal fragments, loose pavement, or dropped tools that pose a danger to aircraft engines and tires.
- For perimeter and runway safety, the AI uses sophisticated object classification to differentiate between various types of threats. It can reliably distinguish a human intruder from a service vehicle or a large animal, like a deer, from a harmless smaller creature. This capability dramatically reduces false alarms. Thermal cameras are exceptionally effective for this task, as they detect the distinct heat signature of a mammal against the cooler ambient temperature of the runway or landscape, even in complete darkness.
Output & Interaction: Immediate Airside Alerts
Upon confirming a threat, the system generates an instant alert for the airside operations or security team. The alert provides the precise GPS location of the threat, a high-resolution image or video clip for verification, and its classification, enabling swift removal or interception.
3.4 Solution 4: AI for Airport Operational Optimization
This module focuses on the core business functions of the airport. It uses AI for airport operations to drive down costs and boost overall productivity.
Data Acquisition: The Digital Pulse of Operations
This system ingests a wide variety_of data sources. These include image scans from baggage conveyor belts, reads from Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) (A technology using radio waves to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects) tags, airline flight schedules, real-time gate availability, and energy consumption data from Internet of Things (IoT) (A network of interconnected physical devices with sensors that collect and exchange data) devices on lighting and HVAC systems.
How does the AI work:-
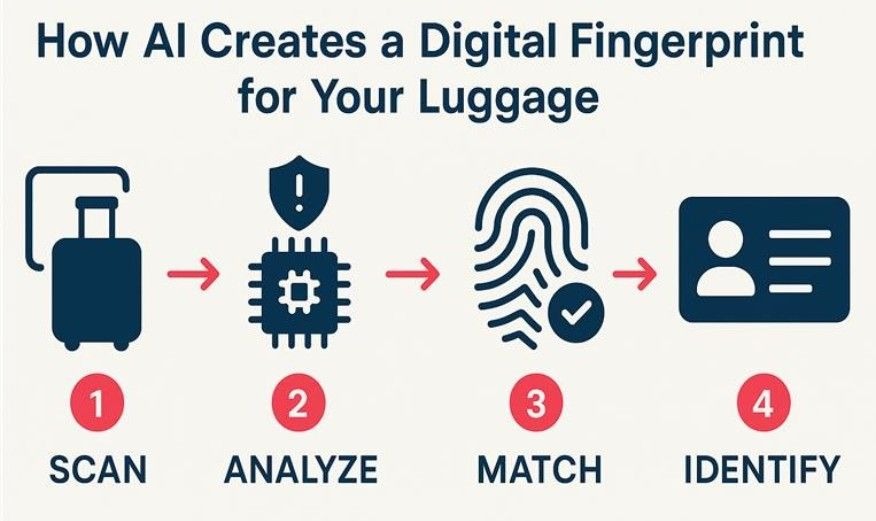
1) Smart Baggage Tracking. As a bag enters the handling system, AI-powered image recognition captures its unique visual characteristics—color, size, shape, and even stickers or dents. This creates a digital fingerprint that is linked to the bag’s RFID tag and the passenger’s flight data. This dual-system approach ensures that even if a paper tag is ripped off, the bag can still be identified visually and tracked. The system follows the bag through every checkpoint, flagging any deviations from its expected path that could signal a mishandling. The adoption of such technologies has proven effective, helping reduce the global rate of mishandled baggage to 6.3 per 1,000 passengers in 2024, a 67% drop since 2007.
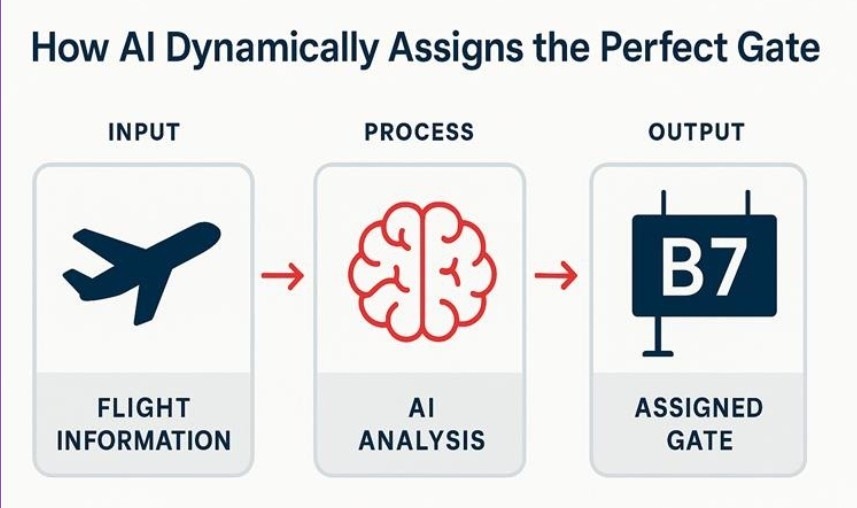
2) Automated Gate Scheduling. An advanced optimization algorithm analyzes real-time flight data, aircraft type, passenger connection times, and current gate availability. It uses sophisticated meta-heuristic algorithms like Tabu Search to dynamically assign aircraft to gates. This process aims to minimize passenger walking distances and maximize the schedule’s resilience against unexpected delays.
3) IoT-Based Energy Monitoring. The system continuously analyzes data from thousands of IoT sensors across the terminal. It uses machine learning to correlate real-time occupancy data (from the crowd management module) with energy usage. It then automatically dims lights and adjusts thermostats in empty or low-traffic areas to eliminate energy waste.
Output & Interaction: An Optimized and Transparent Operation
The results are delivered directly to the relevant stakeholders. Passengers can receive real-time updates on their bag’s location through a mobile app. Ground crews and gate agents get optimized, dynamic schedules sent to their work devices. Facility managers receive dashboards that clearly visualize energy savings and other key operational metrics.
3.5 The Rise of Generative AI for Airports
The newest frontier in aviation technology is generative AI for airports. This technology uses Large Language Models (LLMs) (A type of AI trained on vast amounts of text data to understand and generate new, human-like language) to synthesize complex operational data into clear, concise, and actionable information. This is a key area of development for the future of AI for airports.
Key use cases for generative AI for airports include:
- Automated Operational Reporting. Instead of staff spending hours manually compiling performance reports, a generative AI tool can instantly analyze delay data. It then generates a summary in natural language that identifies root causes and highlights performance trends.
- Enhanced Passenger Communication. Advanced AI chatbots and virtual assistants can handle a vast range of passenger queries 24/7. They can provide information on flight status, baggage allowances, and terminal navigation in multiple languages, freeing human agents to focus on more complex customer service issues.
- Intelligent Disruption Management. During a major flight delay or cancellation, generative AI can automatically create and send personalized communications to every affected passenger. These messages can explain the situation clearly and outline specific rebooking options and entitlements.
4. Our Approach to Build Airport AI Solutions
The prospect of a full-scale AI overhaul can seem daunting, raising valid questions about cost, hardware replacement, and operational disruption. However, the journey to an intelligent airport is not an all-or-nothing leap. It’s a strategic, phased evolution that builds value at every step, starting with the infrastructure you already have.
Our implementation follows a clear, manageable roadmap:
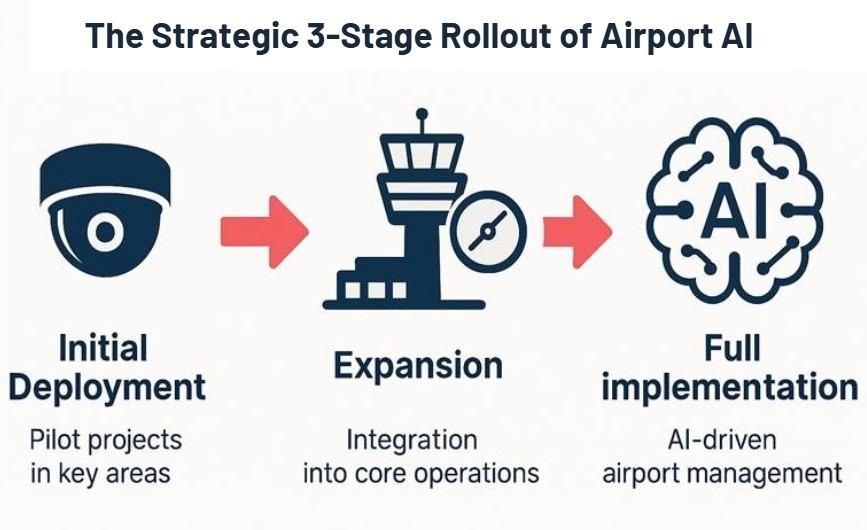
- Stage 1: Activate Your Existing Infrastructure We begin by leveraging your current assets. Your network of CCTV cameras, once passive recorders, becomes the eyes of the new system. We deploy a powerful AI intelligence layer directly on top of this hardware. Using proven computer vision models like YOLO, this layer immediately starts to make sense of the raw video feeds, transforming them from simple recordings into streams of structured, actionable data.
- Stage 2: Prove Value with a Pilot Program Next, we roll out the intelligence in a targeted, controlled manner. We launch a pilot program focused on a single, high-impact pain point—such as security checkpoint queues or unattended luggage detection in a specific terminal. This approach allows you to see a clear return on investment and gain stakeholder confidence with minimal disruption to your daily workflow.
- Stage 3: Scale and Unify into a Collective Brain Each successfully deployed AI module becomes a building block. As we connect these intelligent nodes—security, crowd management, airside safety, operations—they begin to form a single, unified system. This is the ultimate goal: a central, collective brain for the entire airport, providing a holistic, real-time view and unlocking insights that were previously impossible to see.
5. Key Enabling Technologies: The Core of AI for Airports
A suite of powerful and mature technologies forms the foundation of any comprehensive AI for airports platform. Understanding these core components is key to appreciating the system’s capabilities.
- Computer Vision. This is the technology that allows machines to “see” and interpret the world through images and videos. It is the essential engine behind security surveillance, crowd density analysis, and foreign object detection.
- Machine Learning (ML). This is a subset of AI where systems learn from data to identify patterns and make intelligent decisions without being explicitly programmed for every scenario. It powers the predictive forecasting used in passenger flow management and predictive maintenance schedules.
- Deep Learning. This is an advanced form of machine learning that uses complex, multi-layered neural networks. It excels at recognizing highly nuanced patterns, such as identifying a tiny piece of debris on a vast runway or distinguishing subtle, suspicious human behaviors from normal activity.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP). This is the technology that enables computers to understand, interpret, and respond to human language. It is the core technology that powers the conversational abilities of generative AI chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Internet of Things (IoT). This refers to the vast network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, and appliances embedded with sensors that collect and share data. In an airport context, IoT is crucial for real-time energy management and monitoring the status of physical assets.
- Generative AI. This is the branch of AI focused on creating entirely new content, such as text, images, or data summaries. It leverages LLMs to revolutionize how airports communicate with passengers and how operational data is reported and understood.
See what’s possible for your airport
6. Potential Impact & Benefits for the Aviation Industry
Implementing a unified platform for AI for airports translates directly into tangible, high-value benefits that address the industry’s most pressing pain points. The impact extends across safety, efficiency, and passenger satisfaction.

- Enhanced Safety and Security. Proactive threat detection from AI security for airports and continuous airside monitoring drastically reduce the risk of security breaches and safety incidents. This is the most critical benefit of implementing AI for airports.
- Improved Operational Efficiency. Automating complex and time-consuming tasks like gate scheduling and baggage reconciliation significantly reduces aircraft turnaround times. This leads to fewer delays and better on-time performance across the board.
- Significant Cost Reduction. Optimized staff and gate allocation, lower energy consumption (with savings of up to 20% annually), and fewer expenses related to mishandled baggage and FOD-related aircraft damage result in substantial financial savings.
- Superior Passenger Experience. Shorter wait times, access to real-time information about baggage and flight status, and a smoother, less stressful journey from the curb to the gate directly increase passenger satisfaction and build airline loyalty.
- Data-Driven Decision Making. The system equips airport management with the predictive insights needed to shift from a reactive to a proactive operational model. This enables smarter, more effective long-term strategic planning.
Our Recent Work for Aviation Industry
7. Important Considerations for Implementation
While the benefits are compelling, deploying AI for airports is a complex undertaking. A successful implementation requires careful planning and partnership with experienced technical experts who understand these challenges.
- Data Integration and Legacy Systems. A primary hurdle is integrating new AI solutions with an airport’s existing, and often fragmented, technology infrastructure. Gaining access to and harmonizing data from multiple siloed systems is a critical and complex first step.
- Data Privacy and Security. The use of AI for widespread surveillance and passenger tracking raises significant data privacy concerns. Any implementation must include robust data governance policies, anonymization techniques where appropriate, and strict adherence to regulations like GDPR.
- Cost of Implementation. The upfront investment in AI software, computing infrastructure, and specialized training can be substantial. A clear business case with a detailed analysis of the expected return on investment is essential.
- Change Management and Workforce Adaptation. Introducing AI fundamentally changes established workflows and job roles. It requires a strategic approach to reskilling staff, shifting their focus from performing manual tasks to supervising AI systems and handling high-level exceptions.
- Regulatory Compliance and Validation. Aviation is one of the world’s most highly regulated industries. Any AI system that impacts safety or security must undergo rigorous testing and validation to prove its reliability and accuracy. It must comply with standards set by bodies like the FAA, EASA, and ICAO.
8. Tailoring AI for Your Unique Needs with Softlabs Group
The principles of AI for airports are universal, but every airport possesses a unique operational footprint, a distinct set of challenges, and a specific technological landscape. A one-size-fits-all product is rarely the optimal solution. Realizing the full, transformative potential of these advanced technologies requires a bespoke approach tailored to your specific environment.
Softlabs Group specializes in exactly this. Our expertise lies not just in developing powerful AI algorithms, but in understanding the intricate operational realities of our clients. We work with you to analyze your unique requirements, navigate the complex implementation challenges, and build custom, effective, and fully integrated AI solutions. A partnership with Softlabs Group ensures you get a system designed to deliver tangible results and a clear return on investment for your airport.
Ready to solve your specific challenges?
